When automating web applications, handling dropdown menus is a crucial task. Selenium WebDriver, a powerful tool for web automation, provides multiple ways to interact with dropdowns efficiently. In this guide, we will explore various methods to handle dropdowns in Python Selenium with practical examples.
- Selenium Features
- Selenium Installation
- Selenium Locators
- XPath Fundamentals
- CSS Selectors Methods
- Different Browsers Execution
- find_element & find_elements
- Check Enabled Status
- Check Displayed Status
- Check Selected Status
- Selenium Waits
- Send_keys Method
- Click Method
- Get Text
- Get Attribute Value
- Get Current URL
- Forward, Back, Refresh
- Take Screenshot
- Handle Browser Tabs
- Handle iframe
- Mouse Hover
- Context-Click
- Drag & Drop
- Handle Alerts
- Handle Dropdown
- Execute Javascript
- Scroll To element
- Headless Mode Execution
- Chrome Options
- Keyboard Action
What is a Dropdown in Selenium?
A dropdown menu is an HTML element that allows users to select an option from a list. These elements are commonly created using the <select> tag. Selenium provides the Select class to interact with such dropdown elements easily.
Importing Required Libraries
Before handling dropdowns, ensure you have Selenium installed in your Python environment.
Now, import the necessary modules:
from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import Select
Handling Dropdowns Using Selenium
1. Selecting an Option by Visible Text
This is the most common way to select an item from a dropdown. The select_by_visible_text() method is used to select an option based on its displayed text.
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.select import Select
# Initiate Webdriver
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.maximize_window()
driver.implicitly_wait(10)
# Launch dummy website
driver.get("https://automationbysqatools.blogspot.com/2021/05/dummy-website.html")
# Select dropdown one element
drop_down_element = driver.find_element(By.ID, "admorepass")
select_obj = Select(drop_down_element)
# Select dropdown option with select_by_visible_text
select_obj.select_by_visible_text("Add 1 more passenger (100%)")
# Select country dropdown element
country_dd = driver.find_element(By.ID, "billing_country")
select_obj2 = Select(country_dd)
select_obj2.select_by_visible_text("India")
time.sleep(5)
# Close the Browser
driver.close()
2. Selecting an Option by Index
If you know the position of the option, you can select it using select_by_index().
dropdown.select_by_index(2) # Selects the third option (Index starts at 0)
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.select import Select
# Initiate Webdriver
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.maximize_window()
driver.implicitly_wait(10)
# Launch dummy website
driver.get("https://automationbysqatools.blogspot.com/2021/05/dummy-website.html")
# Select add more passenger dropdown element
drop_down_element = driver.find_element(By.ID, "admorepass")
select_obj = Select(drop_down_element)
# Select value by select_by_index() method
select_obj.select_by_index(2)
# Select country dropdown element
country_dd = driver.find_element(By.ID, "billing_country")
select_obj2 = Select(country_dd)
# Select value by select_by_index() method
select_obj2.select_by_index(10)
time.sleep(5)
# Close the Browser
driver.close()
3. Selecting an Option by Value Attribute
Each dropdown option has a value attribute that can be used for selection.
dropdown.select_by_value("option2") # Selects the option with value "option2"
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.select import Select
# Initiate Webdriver
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.maximize_window()
driver.implicitly_wait(10)
# Launch dummy website
driver.get("https://automationbysqatools.blogspot.com/2021/05/dummy-website.html")
# Select add more passenger dropdown element
drop_down_element = driver.find_element(By.ID, "admorepass")
select_obj = Select(drop_down_element)
# Select dropdown option by value option
select_obj.select_by_value("3")
# Select country dropdown element
country_dd = driver.find_element(By.ID, "billing_country")
select_obj2 = Select(country_dd)
select_obj2.select_by_value("BE") # Belarus country
time.sleep(10)
# Close the Browser
driver.close()
4. Getting All Dropdown Options
Sometimes, you may need to extract all options from a dropdown.
options = dropdown.options
for option in options:
print(option.text) # Prints all available options
5. Deselecting Options (For Multi-Select Dropdowns)
If the dropdown allows multiple selections, you can deselect options using:
dropdown.deselect_by_index(1)
dropdown.deselect_by_value("option2")
dropdown.deselect_by_visible_text("Option 3")
dropdown.deselect_all() # Clears all selections
Handling Non-Select Dropdowns
Some dropdowns are not built using the <select> tag. Instead, they rely on div, span, or ul/li elements. In such cases, JavaScript execution or direct element interaction is required.
1. Clicking to Reveal Options and Selecting One
dropdown_button = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, "//div[@class='dropdown']") dropdown_button.click() option_to_select = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, "//li[text()='Option 1']") option_to_select.click()
2. Using JavaScript to Select an Option
For complex dropdowns, JavaScript can be used:
script = "document.querySelector('css-selector-for-dropdown').value='option_value'"
driver.execute_script(script)
Best Practices for Handling Dropdowns in Selenium
- Use explicit waits to ensure the dropdown loads before interaction.
- Handle stale element exceptions if dropdown updates dynamically.
- Use appropriate selection methods based on the dropdown structure.
- Validate selections by retrieving the selected option.
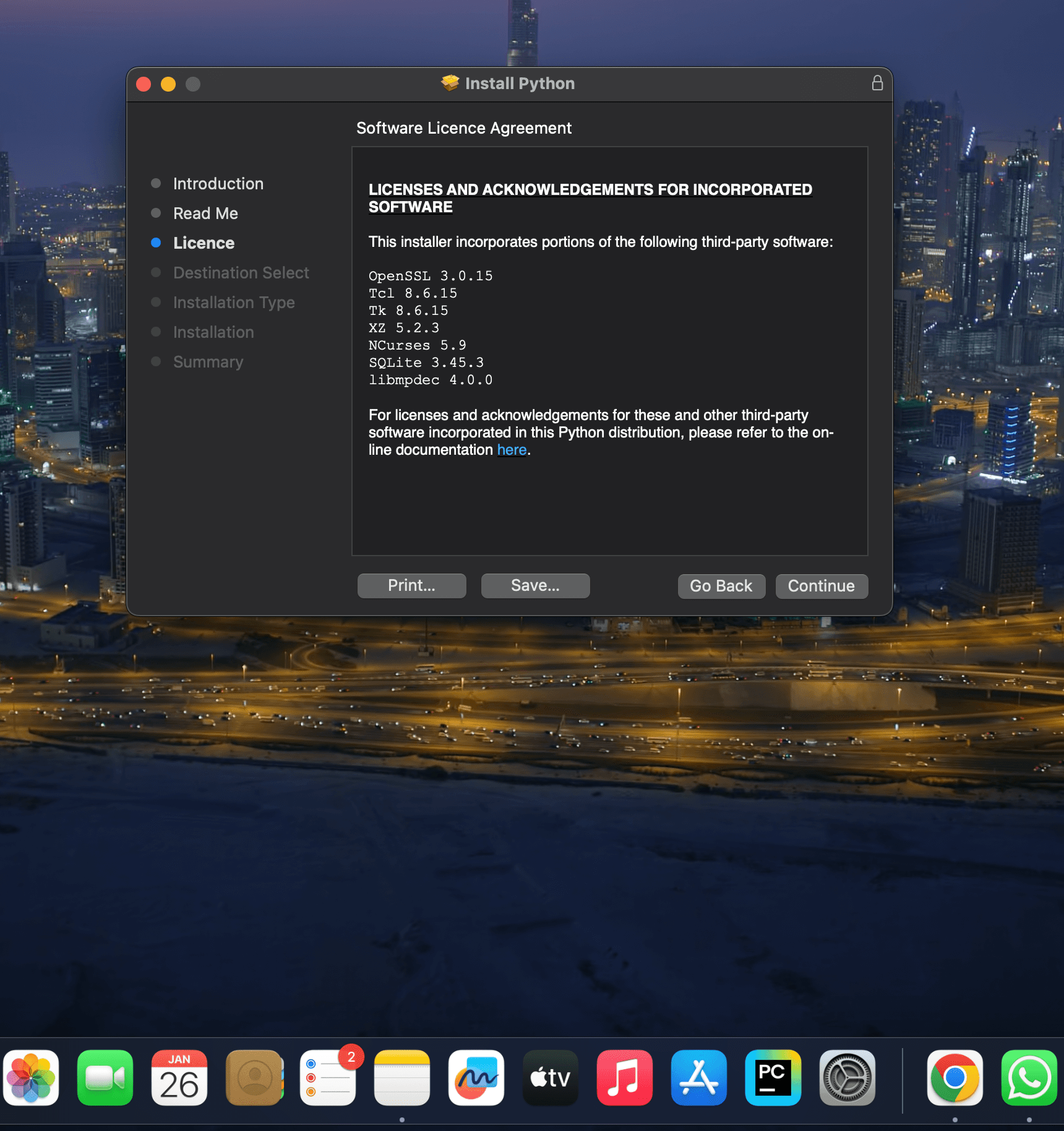
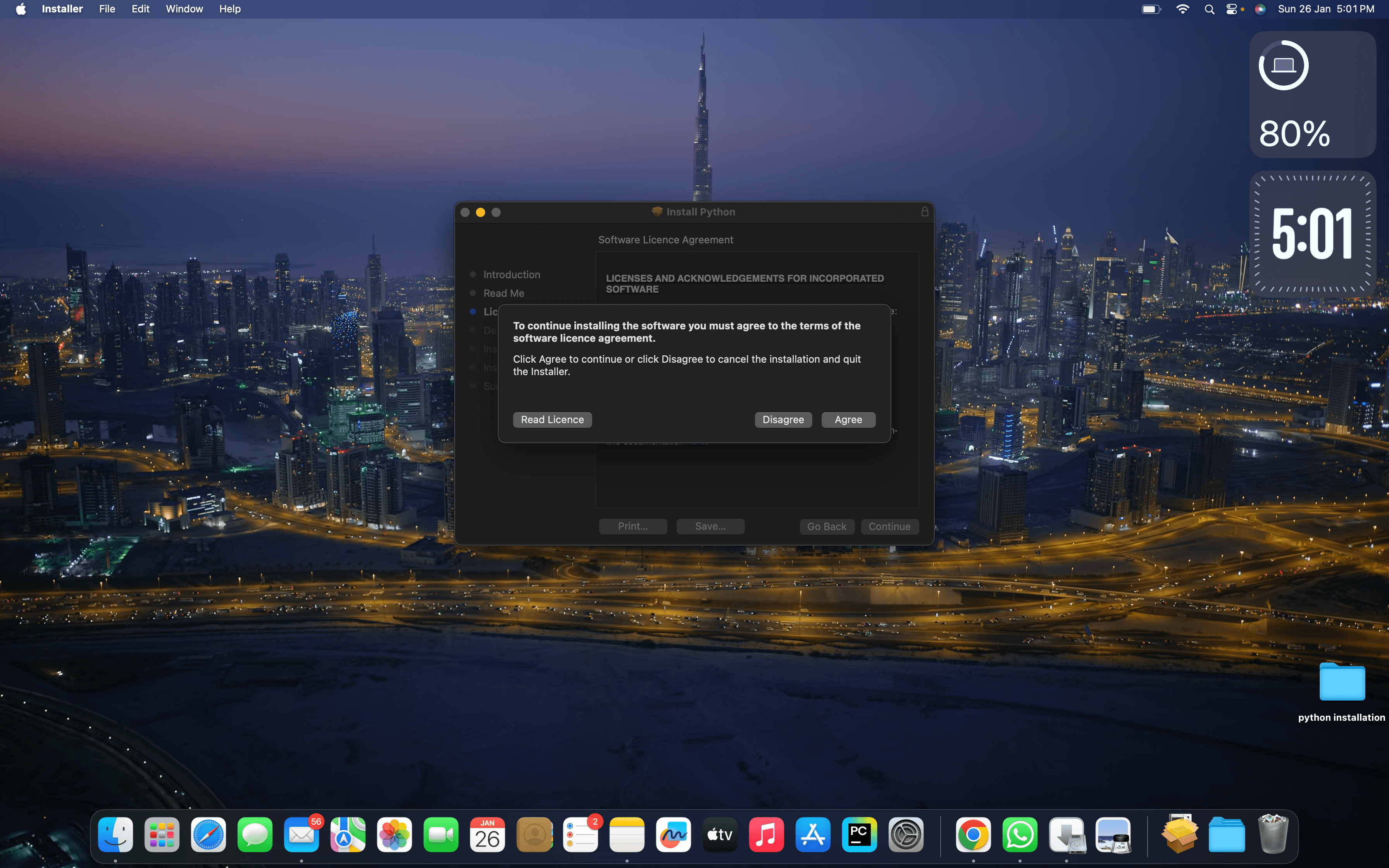
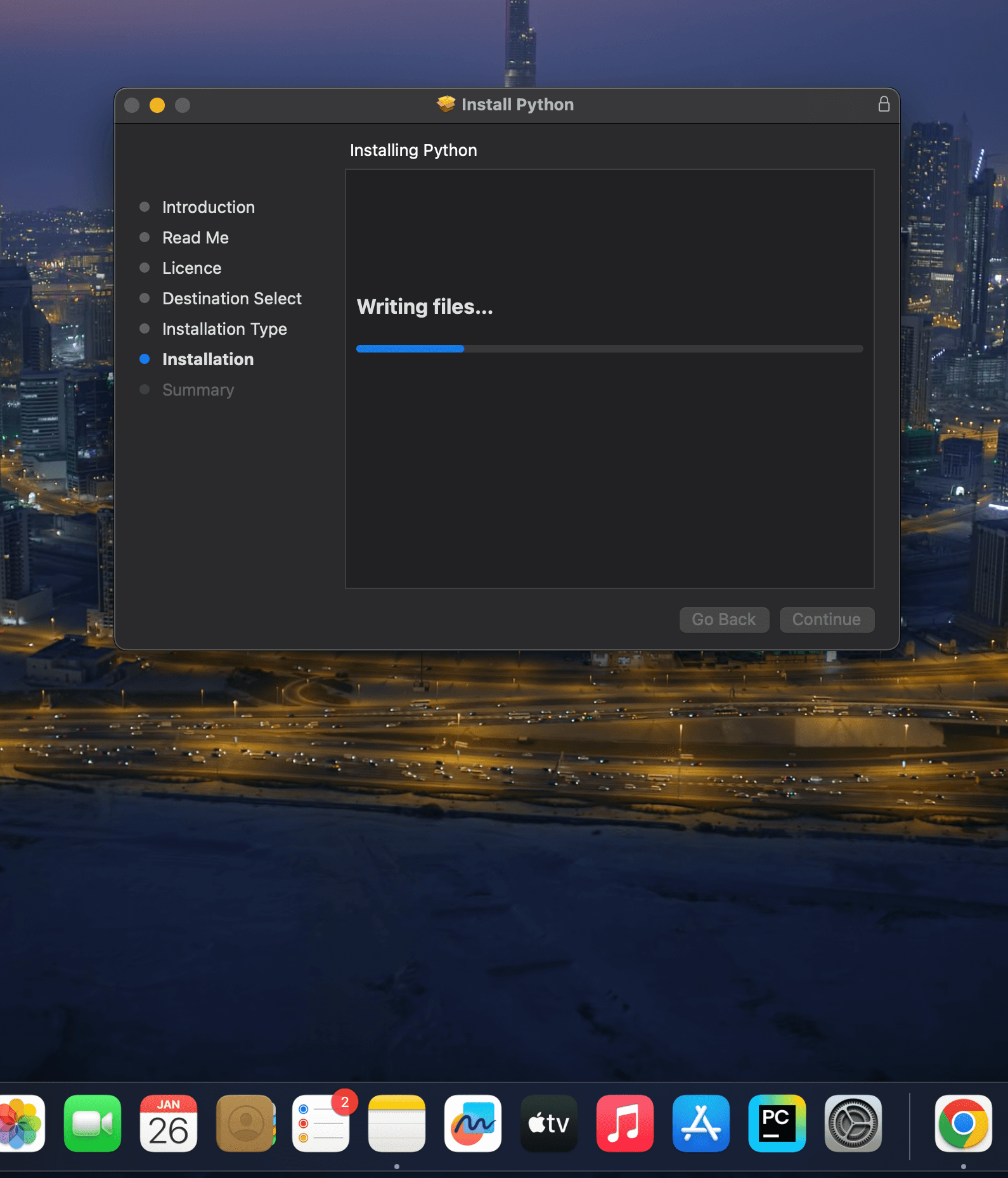
 The installation will begin. This might take a few minutes.
The installation will begin. This might take a few minutes.
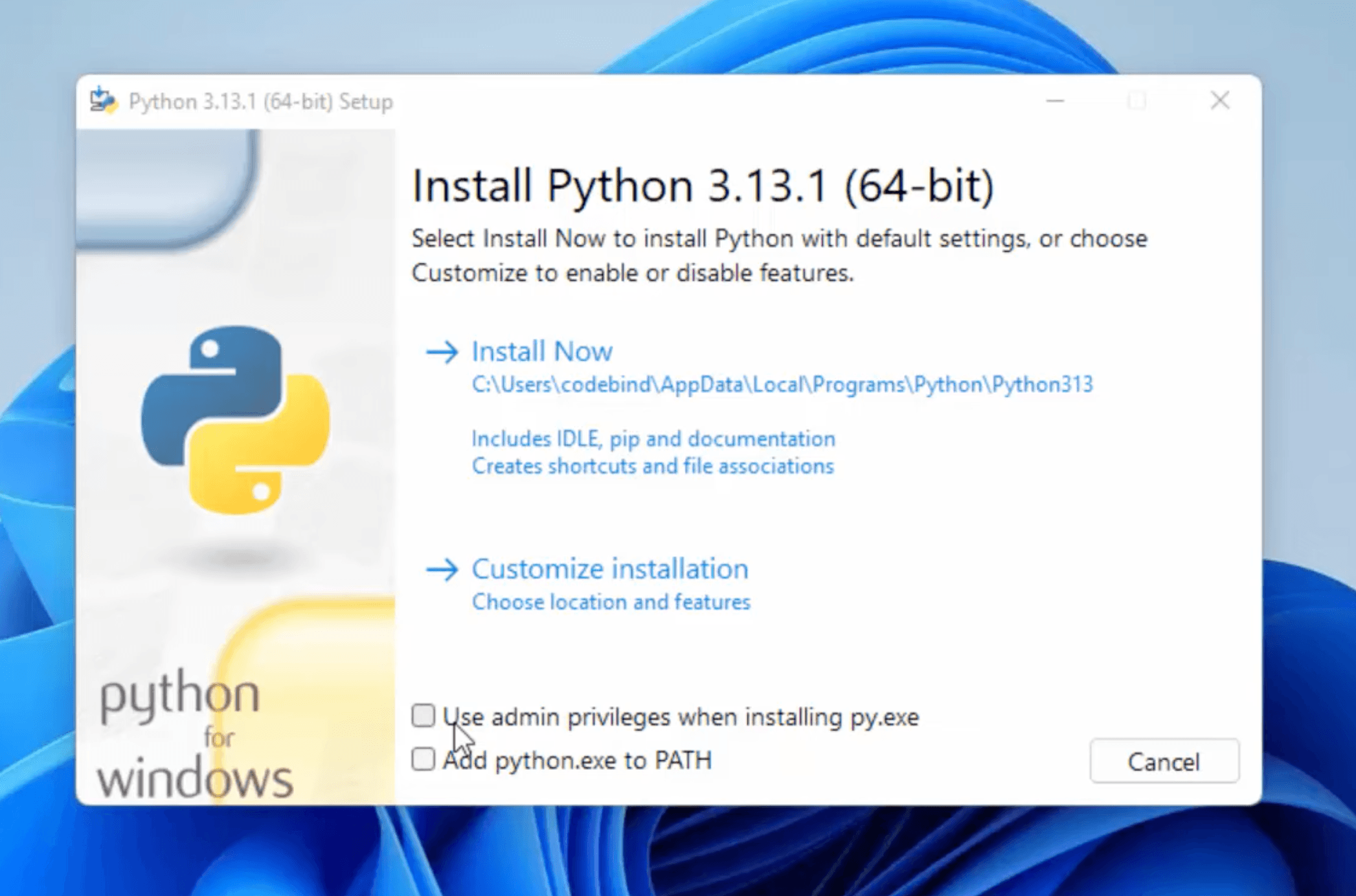
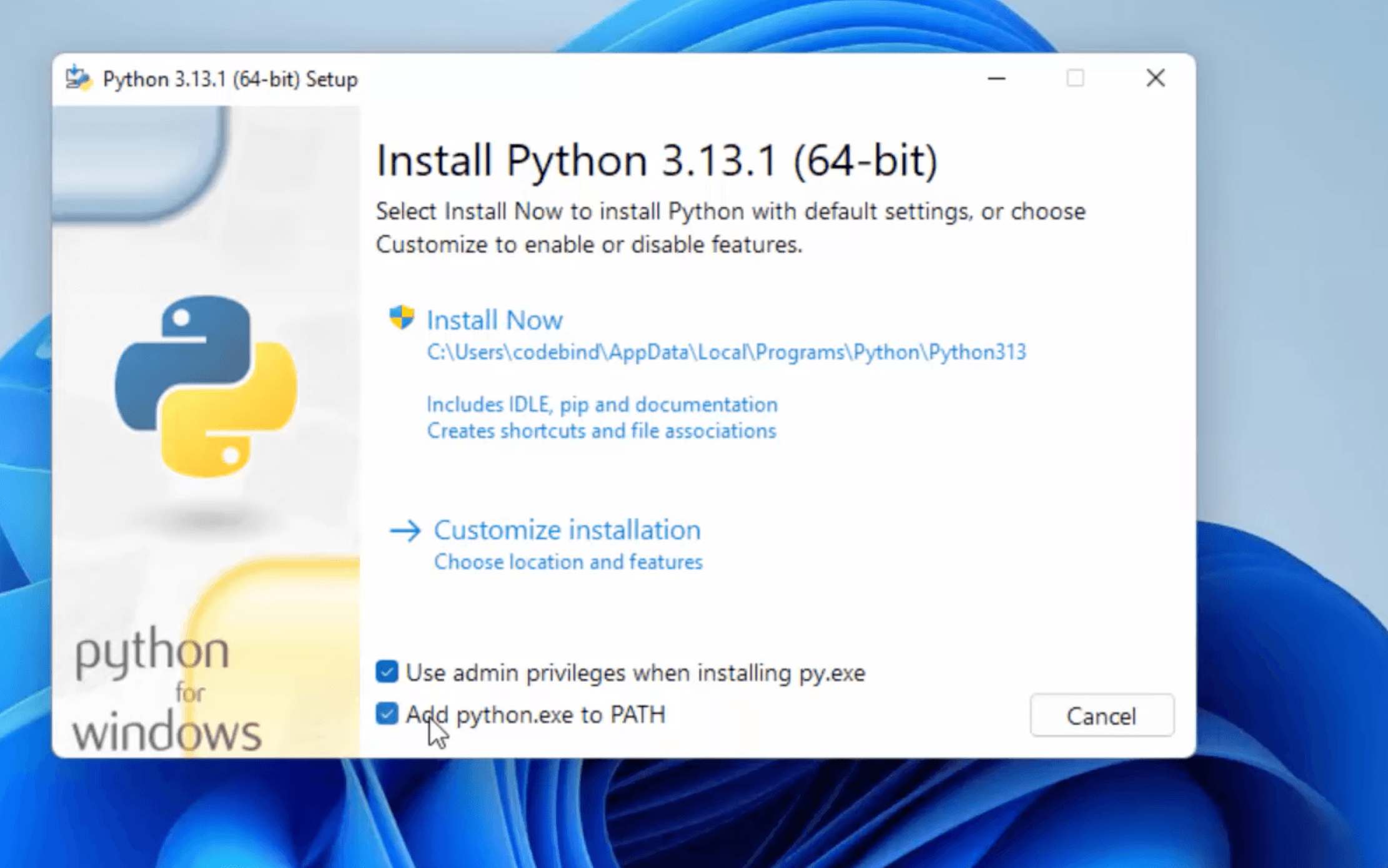
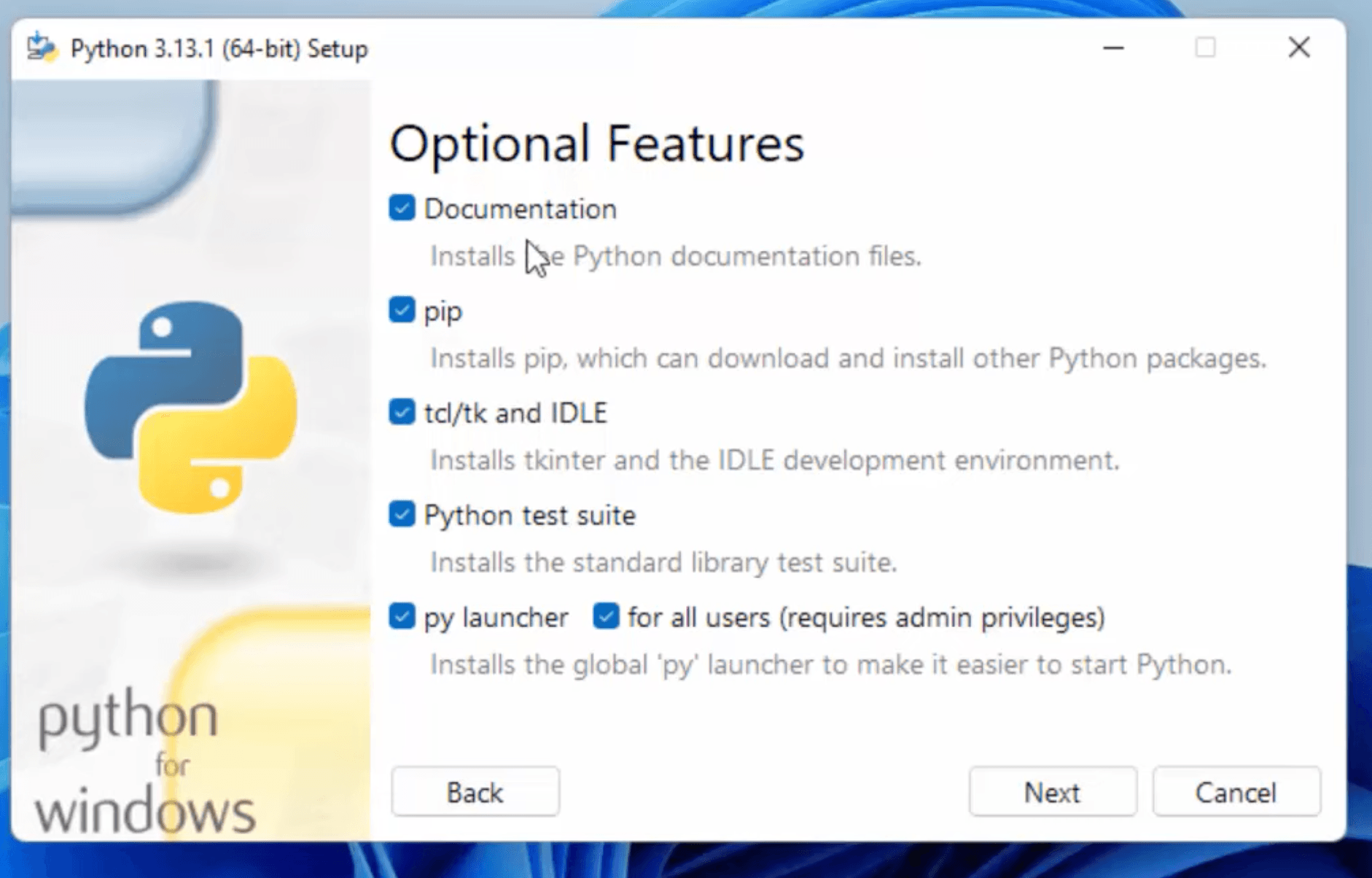
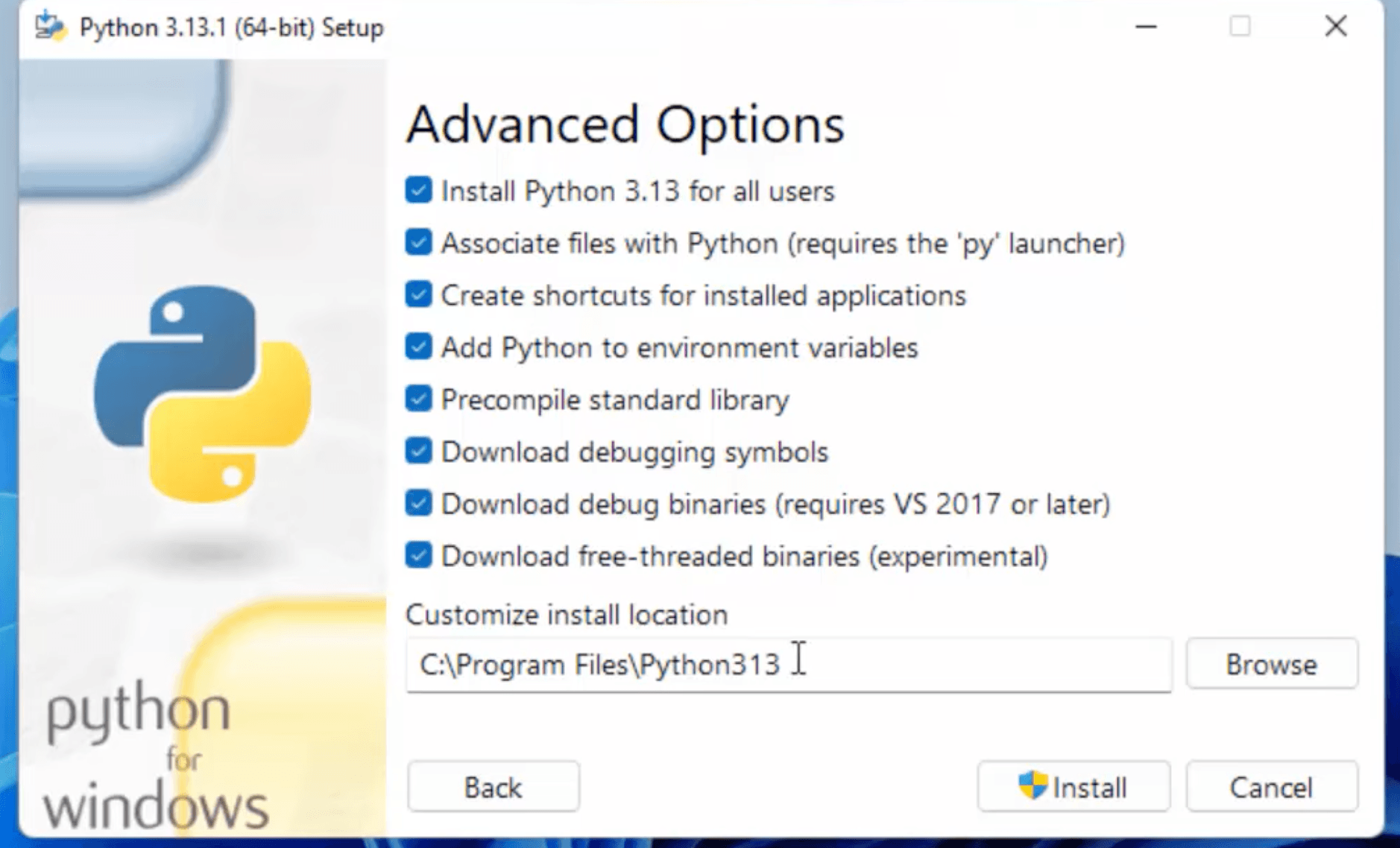
 And move the python installer package to bin
And move the python installer package to bin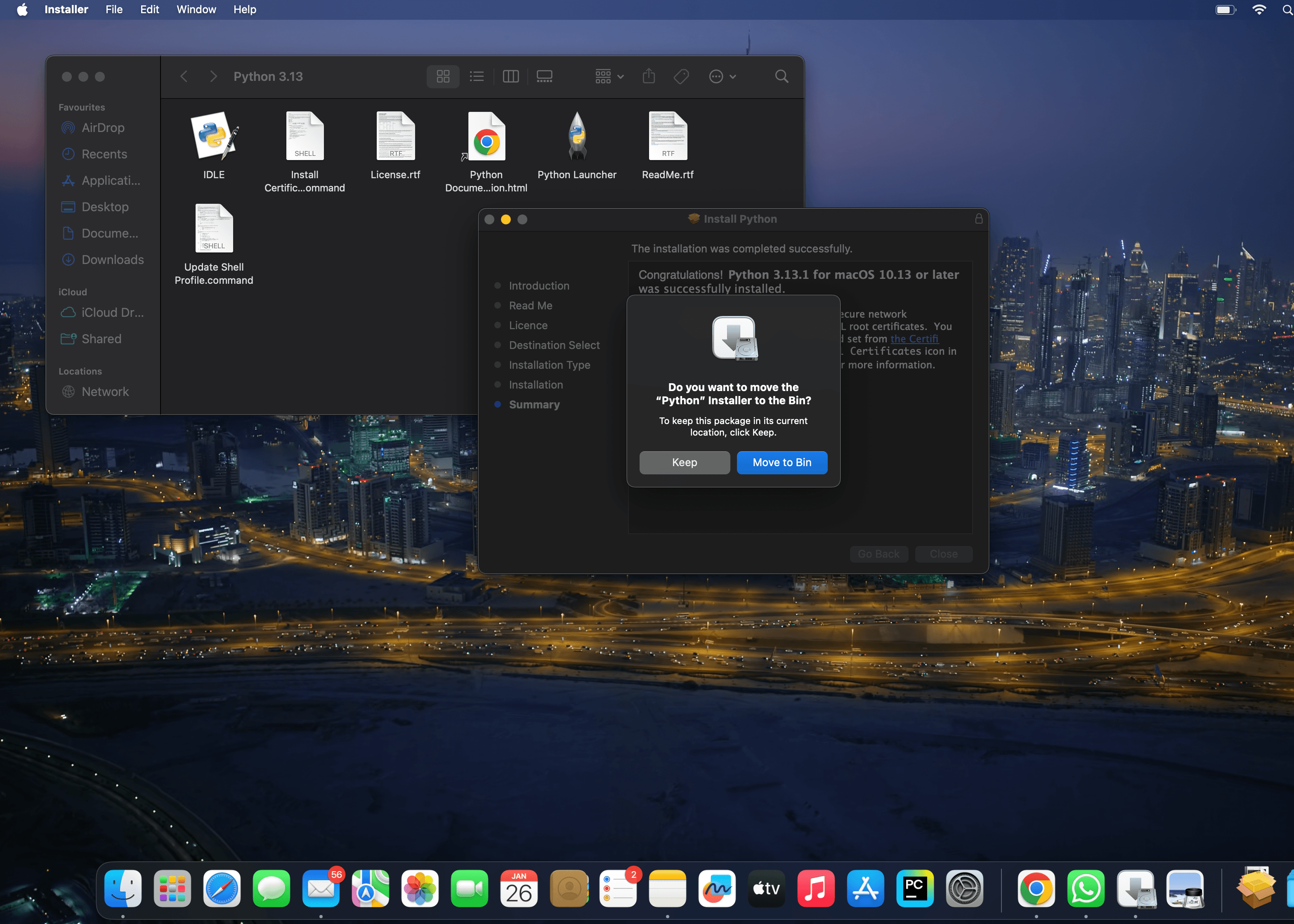
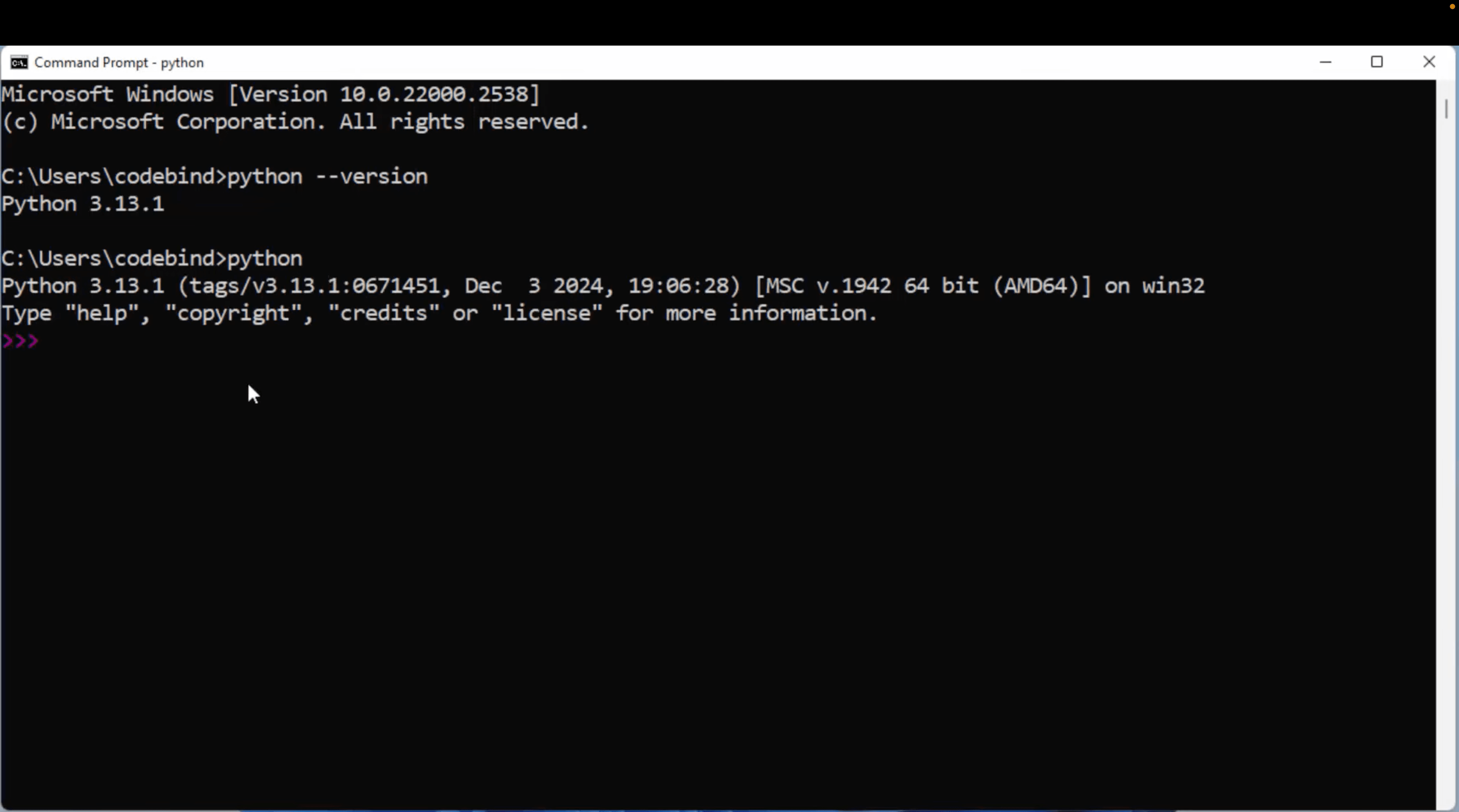
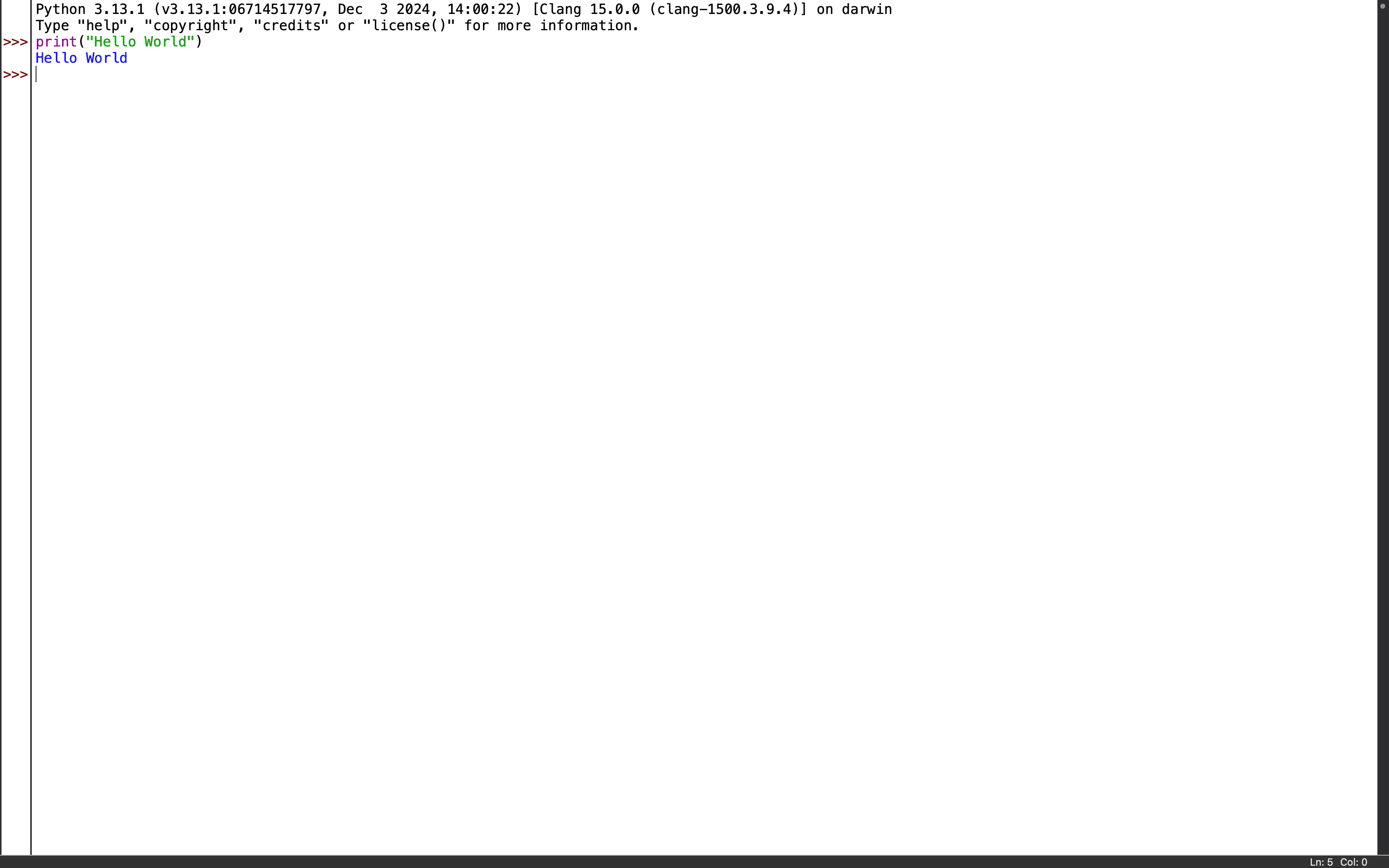 You can also check version in Terminal by giving the following command to check the version of python.
You can also check version in Terminal by giving the following command to check the version of python.